
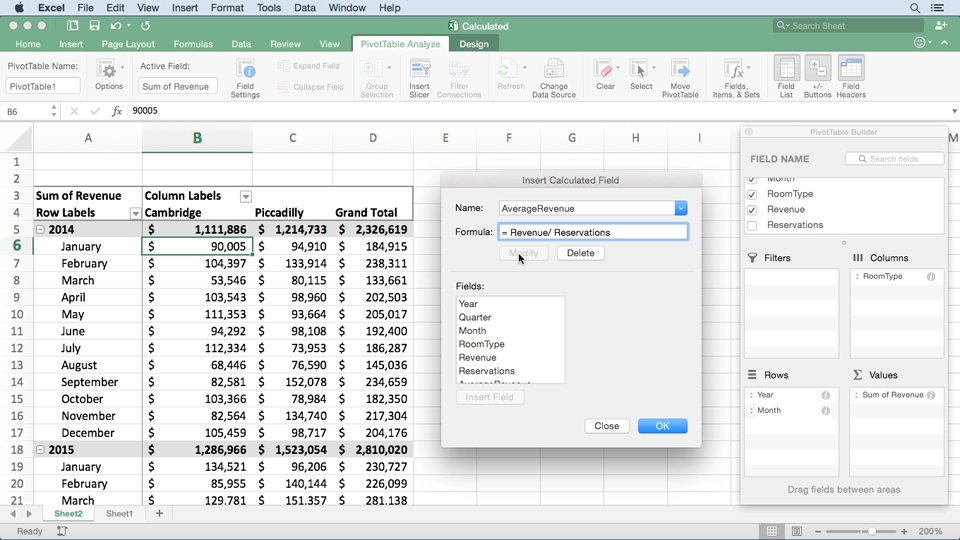
Relational: Return individual, related tables from hierarchical data.FlattenedDocuments: Implicitly join nested documents and their parents into a single table.The data provider returns nested elements as aggregates of data. Document (default): Model a top-level, document view of your XML data.The DataModel property is the controlling property over how your data is represented into tables and toggles the following basic configurations.
See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation for authentication guides.Īfter setting the URI and providing any authentication values, set DataModel to more closely match the data representation to the structure of your data. The major authentication schemes are supported, including HTTP Basic, Digest, NTLM, OAuth, and FTP. See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation to authenticate to your data source: The data provider models XML APIs as bidirectional database tables and XML files as read-only views (local files, files stored on popular cloud services, and FTP servers). Modifying iODBC's system-wide settings requires elevated permissions to do so, you can use following to open a text editor from the terminal: You can find the correct odbc.ini in the following paths: System data sources can be accessed by all users. User data sources can only be accessed by the user account whose home folder the odbc.ini is located in. You can define ODBC data sources in sections in the odbc.ini file.
To activate a trial license, omit the key input.Ĭd "/Applications/CData ODBC Driver for XML/bin" In a terminal run the following commands to license the driver. This makes the driver easy to use with these tools. The CData ODBC Driver for XML is preconfigured for the iODBC driver manager, as are many other products like Microsoft Excel. Installing the CData ODBC Drivers on Mac OS X This article walks through creating a DSN for XML data in iODBC and accessing XML data in Microsoft Excel, all on a machine running Mac OS X.
Microsoft Excel features calculations, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language that allows users to work with data in many of the ways that suit their needs, whether on a Windows machine or a Macintosh machine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
